The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an institution that was created in 1945 at the Bretton Woods conference in order to ensure economic cooperation between countries of the world, and the stability of global financial system. Based in Washington DC It is governed by its 185 Member States, covering virtually every country in the world, in front of which everyone is responsible. It has a developmental role in the global economy, by offering various countries such knowledge and expertise in the financial world. The IMF seeks to avoid errors that could lead to a global financial crisis.
In the status of the IMF missions are listed as follows:
– To promote international monetary cooperation
– Facilitating the expansion and balanced growth of world trade
– Promote exchange stability
– Assist in establishing a multilateral system of payments – Put its resources (subject to adequate safeguards) available to countries facing difficulties in their balance of payments
Key numbers of the IMF :
- Number of members : 185 countries
- Chairman : Dominique Strauss Kahn since November 2007
- Number of employees: 2700
- Operating budget : 980 millions of Euro
- Quota : 352 billions of dollars (march 2008)
- Outstanding loans : 16.1 billions of dollars to 64 different countries
IMF Functioning
The IMF is governed by its 185 countries members, each with a vote weighted by its financial contribution to the organization (its “quota”). It takes many decisions in consultation with the World Bank within the “Development Committee.” Its current management is entrusted to a board of directors composed of the President of the organization and 24 directors representing each nation. 8 of them have a permanent representative (United States, United Kingdom, France, Germany, Japan, China, Russia and Saudi Arabia), the other are elected by permanent members.
Most decisions are taken in practice at the unanimity. However, given the terms of decision making within the IMF, which require a qualified majority corresponding to 85% of voting rights, the United States or the European Union as a whole, have a veto power over IMF decisions because they each have over 15% of voting rights. However, EU countries are not always coordinated.
It is currently Dominique Strauss Kahn, a French which is at the head of the IMF.
IMF Funding
The IMF plays a role of financial intermediary between States Members. Thus, each state must pay the organization a certain sum, named “quota” and whose amount is determined by its economic power, itself measured by GNP and the importance of foreign trade. 25% of this quota shall be paid in gold, the remainder in national currency. In case of imbalance in its balance of payments that may endanger the monetary equilibrium on the foreign exchange market, each country member can automatically get 25% of its quota ( “Drawing Right”), enabling it to support, through the purchase, the domestic currency. If the IMF judges it necessary, it can lend to this country until 125% of its quota. Its loans are expected to allow central banks to defend their currencies on the foreign exchange market.
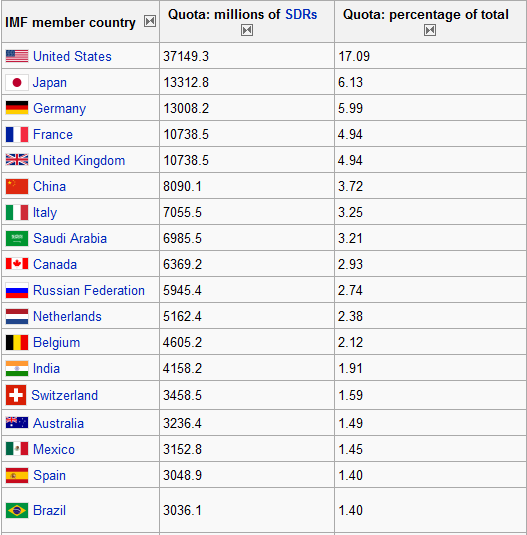
The mode of decision of the IMF, like the World Bank, is based on an allocation of voting rights based on the amount of the contribution of states member on a “1 dollar, 1 vote”. However, voting rights differ slightly to quotas, minimum voting being assigned to all countries, even smaller. The assessments of the main contributors to the Fund are as follows, after the raising of assessments of China, South Korea, Mexico and Turkey in September 2006:
The IMF resources related to assessments are approximately SDR 210 billion (300 billion U.S. dollars), plus the opportunity for the IMF to borrowing against major economic powers (these credits are around 50 billion dollars). At the G20 meeting in London April 2, 2009 it was decided to increase significantly the resources of the IMF up to 1 000 billion dollars to help cope with the global crisis.
IMF Activities
Even if he has a strong political impact, the IMF is sometimes not listening when the economy goes well. He still gives regular advice to states on policies to be adopted or to make reforms. When a state has financial difficulties and that economic agents do not want to take the risk to lend money, the IMF intervenes and lend him. But this has a condition, it shall submit to the State a list of reforms that must be apply in return. Again, the IMF plays a role in stability of the financial system, either a national or global. It also participates in the fight against poverty by helping some economically underdeveloped countries. Another role of the IMF is to ensure the stability of exchange rates to preserve the development of world trade. To achieve these objectives, it has therefore three main functions: surveillance, technical assistance and lending operations.
1 – Surveillance
The surveillance includes the dialogue that the IMF maintains with each State Member and policy advices it provides. At regular intervals (usually once per year), the IMF assesses in detail the economic situation of each country. He is discussing with the authorities if economic policies are more conducive to internal and external stability, including to promote orderly growth, and offer advice if necessary. The decision to publish the evaluation reports of the IMF belongs to each country member concerned: the overwhelming majority of countries chooses transparency and disseminate to the public detailed information on bilateral surveillance they are subject to. In addition, the IMF relies on information obtained during the various consultations to draw up balance sheets and draw viewpoint in regional and global levels. He published this work twice a year in the Economic Outlook and the Global Report on financial stability in the world.
2 – Technical assistance
The IMF provides to countries technical assistance and training – free in most cases – to help them strengthen their capacity to design and implement effective policies. Technical assistance includes the fiscal policy, monetary policy and exchange control and regulation of the banking and finance, and statistics.
In most of case of low-income countries, this assistance is based on the Poverty Reduction Strategy Papers (PRSPs). Prepared by the national authorities – in consultation with civil society and external partners for development – the PRSP presents the overall framework of economic policy, structural and social implementation to promote growth and reduce poverty in the country concerned.
3 – Lending operations
The IMF is also a fund to which countries member can use in case of difficulties in balance of payments, to help their recovery. The granting of these funds is subject to conditions and the applicant countries should adopt a policy adjustment advised by the organization to address the causes of the depreciation of its currency.
Through its financial assistance, the IMF give to States Member the breathing space they need to resolve their problem of balance of payments. An economic program supported by the IMF was designed by the national authorities in close cooperation with the institution, and financial aid are contingent on the realization of this program.